California State Assembly
| California State Assembly | |
 | |
| General Information | |
| Party control: | Democrat |
| Session start: | January 3, 2024 |
| Session end: | August 30, 2024 |
| Term length: | 2 years |
| Term limits: | 12 years[1][2] |
| Redistricting: | Commission |
| Salary: | $122,694/year + per diem |
| Members | |
| Total: | 80 |
| Democrats: | 62 |
| Republicans: | 18 |
| Other: | 0 (independent) |
| Vacancies: | 0 |
| Leadership | |
| Speaker: | Robert Rivas (D) |
| Maj. Leader: | Eloise Gomez Reyes (D) |
| Min. Leader: | James Gallagher (R) |
| Elections | |
| Last election: | November 8, 2022 |
| Next election: | November 5, 2024 |
The California State Assembly is the lower chamber of the California State Legislature. Alongside the California State Senate, it forms the legislative branch of the California state government and works alongside the governor of California to create laws and establish a state budget. Legislative authority and responsibilities of the California State Assembly include passing bills on public policy matters, setting levels for state spending, raising and lowering taxes, and voting to uphold or override gubernatorial vetoes.
The California State Assembly meets in the state capitol building in Sacramento, California.
California has a Democratic trifecta. The Democratic Party controls the office of governor and both chambers of the state legislature. |
This page contains the following information on the California State Assembly.
- Which party controls the chamber
- The chamber's current membership
- Partisan control of the chamber over time
- Elections in the chamber and how vacancies are filled
- A district map
- How redistricting works in the state
- Legislation currently under consideration
- Legislative session dates
- Legislative procedures, such as veto overrides and the state budget process
- A list of committees
Party control
Current partisan control
The table below shows the partisan breakdown of the California State Assembly as of January 2024:
| Party | As of January 2024 | |
|---|---|---|
| Democratic Party | 62 | |
| Republican Party | 18 | |
| Independent | 0 | |
| Vacancies | 0 | |
| Total | 80 | |
Members
Leadership
The speaker of the Assembly presides over the Assembly in the chief leadership position, controlling the flow of legislation and committee assignments. The speaker is elected by the majority party caucus, followed by confirmation of the full Assembly on passage of a floor vote. Other Assembly leaders, such as the majority and minority leaders, are elected by their respective party caucuses according to each party's strength in the chamber.[3]
Leadership and members
- Speaker of the Assembly: Robert Rivas (D)
- Majority leader: Eloise Gomez Reyes (D)
- Minority leader: James Gallagher (R)
Salaries
- See also: Comparison of state legislative salaries
| State legislative salaries, 2023 | |
|---|---|
| Salary | Per diem |
| $122,694/year | $214/day |
Swearing in dates
California legislators assume office the first Monday in the December following their election.
Membership qualifications
According to Article IV of the California Constitution:
| “ | A person is ineligible to be a member of the Legislature unless the person is an elector and has been a resident of the legislative district for one year, and a citizen of the United States and a resident of California for 3 years, immediately preceding the election, and service of the full term of office to which the person is seeking to be elected would not exceed the maximum years of service permitted by subdivision (a) of this section.[4][5] | ” |
Historical party control
Democrats won control of the California State Assembly in 1996. In 2022, they won a 62-18 majority.
The table below shows the partisan history of the California Assembly following every general election from 1992 to 2022. All data from 2006 or earlier comes from Michael Dubin's Party Affiliations in the State Legislatures (McFarland Press, 2007). Data after 2006 was compiled by Ballotpedia staff.
California State Assembly election results: 1992-2022
| Year | '92 | '94 | '96 | '98 | '00 | '02 | '04 | '06 | '08 | '10 | '12 | '14 | '16 | '18 | '20 | '22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democrats | 48 | 39 | 44 | 48 | 50 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 51 | 52 | 56 | 52 | 55 | 60 | 60 | 62 |
| Republicans | 32 | 40* | 36 | 32 | 30 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 29 | 28 | 24 | 28 | 25 | 20 | 19 | 18 |
| Independents | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Before 1992
Republicans controlled the assembly from 1942 to 1956. Between 1958 and 1994, the only election where Republicans won a majority was 1968, the same year that Republican Richard Nixon became the first native Californian to be elected president.
Trifecta history
A state government trifecta is a term that describes single party government, when one political party holds the governor's office and has majorities in both chambers of the legislature in a state government. Between 1992 and 2023, California was under the following types of trifecta control:
- Democratic trifecta: 1999-2003, 2011-2023
- Republican trifecta: None
- Divided government: 1992-1998, 2004-2010
California Party Control: 1992-2024
Nineteen years of Democratic trifectas • No Republican trifectas
Scroll left and right on the table below to view more years.
| Year | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governor | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | D | D | D | D | D | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| Senate | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| Assembly | D | D | D | S | R | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
Elections
Elections by year
California state assembly members serve two-year terms, with all seats up for election every two years. California holds elections for its legislature in even years.
2024
Elections for the California State Assembly will take place in 2024. The general election is on November 5, 2024. A primary is March 5, 2024. The filing deadline was December 8, 2023.
2022
Elections for the California State Assembly took place in 2022. The general election was on November 8, 2022. A primary was scheduled for June 7, 2022. The filing deadline was March 11, 2022.
In the 2022 elections, Democrats increased their majority in the California State Assembly.
| California State Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 8, 2022 | After November 9, 2022 | |
| Democratic Party | 60 | 62 | |
| Republican Party | 19 | 18 | |
| Independent | 1 | 0 | |
| Total | 80 | 80 | |
2020
Elections for the office of California State Assembly took place in 2020. The general election was held on November 3, 2020. A primary was scheduled for March 3, 2020. The filing deadline was December 6, 2019.
In the 2020 elections, Democrats held their majority in the California State Assembly from 61-17 to 60-19.
| California State Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 3, 2020 | After November 4, 2020 | |
| Democratic Party | 61 | 60 | |
| Republican Party | 17 | 19 | |
| Independent | 1 | 1 | |
| Vacancy | 1 | 0 | |
| Total | 80 | 80 | |
2018
Elections for the California State Assembly took place in 2018. A top-two primary election took place on June 5, 2018, and the general election was held on November 6, 2018. The candidate filing deadline was March 9, 2018. The filing deadline for write-in candidates was May 22, 2018.[6]
In the 2018 elections, Democrats increased their majority in the California State Assembly from 55-25 to 60-20.
| California State Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 6, 2018 | After November 7, 2018 | |
| Democratic Party | 55 | 60 | |
| Republican Party | 25 | 20 | |
| Total | 80 | 80 | |
2016
Elections for the California State Assembly took place in 2016. The primary election was held on June 7, 2016, and the general election was held on November 8, 2016. The candidate filing deadline was February 25, 2016, for candidates filing with signatures. The deadline for candidates using a filing fee to qualify was March 11, 2016.[7] All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2016.
Heading into the election, Democrats held a 52-28 majority. Democrats gained three seats in the election, giving them a 55-25 majority.
| California State Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | As of November 7, 2016 | After November 8, 2016 | |
| Democratic Party | 52 | 55 | |
| Republican Party | 28 | 25 | |
| Total | 80 | 80 | |
| Click [show] to see election information dating back to 2000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2014Elections for the California State Assembly took place in 2014. A primary election took place on June 3, 2014. The general election was held on November 4, 2014. The signature filing deadline for candidates wishing to run in this election was March 7, 2014. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2014. Heading into the election, Democrats held a 55-24 majority. Democrats lost three seats in the election, giving them a 52-28 majority.
2012Elections for the office of California State Assembly took place in 2012. The primary election was held on June 5, 2012, and the general election was held on November 6, 2012. The candidate filing deadline was March 9, 2012. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2012. Heading into the election, Democrats held a 52-28 majority. Democrats gained four seats in the election, giving them a 56-24 majority.
The table below details the 10 districts with the smallest margin of victory in the November 6 general election in 2012.
2010Elections for the office of California State Assembly took place in 2010. The primary election was held on June 8, 2010, and the general election was held on November 2, 2010. The candidate filing deadline was February 25, 2010. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2010. Heading into the election, Democrats held a 50-27 majority. Democrats gained two seats in the election, giving them a 52-28 majority.
In the 2010 elections, the candidates running for the Assembly raised a total of $77,405,341 in campaign funds. Their top 10 contributors were:[8]
2008Elections for the California State Assembly consisted of a primary election on June 3, 2008, and a general election on November 4, 2008. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2008. During the 2008 election, the total value of contributions to Assembly candidates was $84,390,298. The top 10 contributors were:[9]
2006Elections for the California State Assembly consisted of a primary election on June 6, 2006, and a general election on November 7, 2006. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2006. During the 2006 election, the total value of contributions to Assembly candidates was $91,726,959. The top 10 contributors were:[10]
2004Elections for the California State Assembly consisted of a primary election on March 2, 2004, and a general election on November 2, 2004. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2004. During the 2004 election, the total value of contributions to Assembly candidates was $94,287,806. The top 10 contributors were:[11]
2002Elections for the California State Assembly consisted of a primary election on March 5, 2002, and a general election on November 5, 2002. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2002. During the 2002 election, the total value of contributions to Assembly candidates was $73,822,064. The top 10 contributors were:[12]
2000Elections for the California State Assembly consisted of a primary election on March 7, 2000, and a general election on November 7, 2000. All 80 Assembly seats were up for election in 2000. During the 2000 election, the total value of contributions to Assembly candidates was $85,228,873. The top 10 contributors were:[13]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Term limits
- See also: State legislatures with term limits
The California legislature is one of 16 state legislatures with term limits. Since the passage of Prop 28 in 2012, legislators first elected on or after November 6, 2012, are limited to a maximum of 12 years of service. Prop 140, passed in 1990, affects any members elected prior to November 6, 2012, limiting them to a maximum of three two-year terms (six years total).[14]
Vacancies
If there is a vacancy in the California State Legislature, the governor must call for a special election. The election must be called by the governor within 14 days of the vacancy. No special election can be held if the vacancy happens in an election year and the nominating deadline has already passed.[15]
![]() See sources: California Code, 1773 and California Cons. Art. IV, § 2
See sources: California Code, 1773 and California Cons. Art. IV, § 2
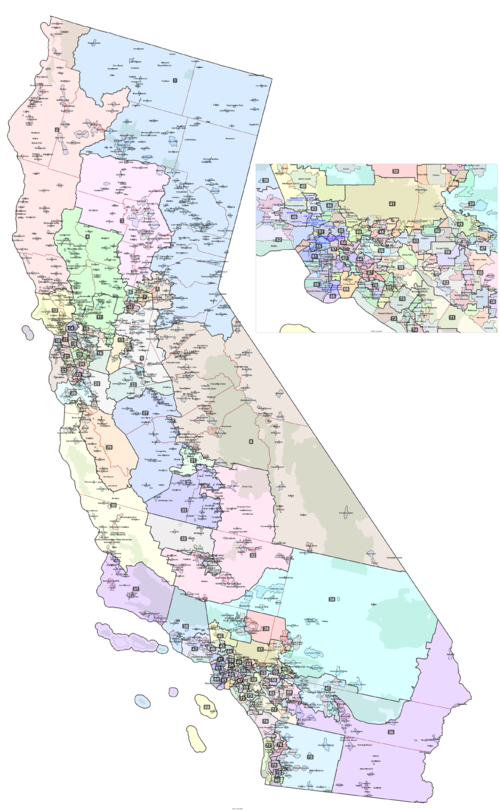
District map
- See also: California state legislative districts
The state of California has 80 state Assembly districts. Each district elects one assembly member.
Use the interactive map below to find your district.
Redistricting
- See also: Redistricting in California
In California, a non-politician commission draws both congressional and state legislative district lines. Established in 2008 by ballot initiative, the commission comprises 14 members: five Democrats, five Republicans, and four belonging to neither party. A panel of state auditors selects the pool of nominees from which the commissioners are appointed. This pool comprises 20 Democrats, 20 Republicans, and 20 belonging to neither party. The majority and minority leaders of both chambers of the state legislature may each remove two members from each of the aforementioned groups. The first eight commission members are selected at random from the remaining nominees. These first eight comprise three Democrats, three Republicans, and two belonging to neither party. The first eight commissioners appoint the remaining six, which must include two Democrats, two Republicans, and two belonging to neither party.[16]
Commissioners must meet the following requirements in order to serve:[16]
- Members must have voted in at least two of the last three statewide elections.
- Members cannot have switched party affiliation for at least five years.
- "Neither commissioners nor immediate family may have been, within 10 years of appointment, a candidate for federal or state office or member of a party central committee; an officer, employee, or paid consultant to a federal or state candidate or party; a registered lobbyist or paid legislative staff; or a donor of more than $2,000 to an elected candidate."
- Members cannot be "staff, consultants or contractors for state or federal government" while serving as commissioners. The same prohibition applies to the family of commission members.
In order to approve a redistricting plan, nine of the commission's 14 members must vote for it. These nine must include three Democrats, three Republicans, and three belonging to neither party. Maps drawn by the commission may be overturned by public referendum. In the event that a map is overturned by the public, the California Supreme Court must appoint a group to draw a new map.[16]
The California Constitution requires that districts be contiguous. Further, the state constitution mandates that "to the extent possible, [districts] must ... preserve the geographic integrity of cities, counties, neighborhoods and communities of interest." Districts must also "encourage compactness." State Senate and Assembly districts should be nested within each other where possible.[16]
2020
The California Citizens Redistricting Commission voted 14-0 in favor of a new state Assembly and Senate district maps on December 20, 2021, and delivered those maps to the secretary of state on December 27, 2021.[17][18] These maps took effect for California's 2022 state legislative elections.
District map after 2020 redistricting
This map took effect for California's 2022 legislative elections.
Click here to view a larger version of this map.
2010
The redistricting commission had until August 15, 2011 to create the maps that would govern the Congressional and legislative districts until 2020. The Commission successfully certified its final maps and handed them over to the Secretary of State on August 15, 2011.[19] These maps went into effect in time for the June 5, 2012 primary.[20]
Sessions
Legislation
The legislation tracker below displays all legislation that the California State Assembly has approved in its most recent legislative session—this includes legislation that has been sent from the Assembly to the Senate and legislation that has already been approved by both chambers and signed by the governor. The table below includes the bill number, its name, progress, most recent action date, and sponsor. Scroll up and down and side to side to see more. Click the bill number to read the bill text and see its voting history. Click the headings to sort the content. Rearrange the order of the headings by clicking and dragging them. Click the magnifying glass in the bottom left corner to search for specific terms. The legislation tracker is maintained and updated by BillTrack50.
Dates of legislative sessions in California by year
2024
- See also: 2024 California legislative session and Dates of 2024 state legislative sessions
In 2024, the legislature was scheduled to convene on January 3, 2024, and adjourn on August 30, 2024.
2023
In 2023, the legislature was scheduled to convene on December 5, 2022, and adjourn on September 14, 2023.
| Click [show] for past years' session dates. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
2022In 2022, the legislature was scheduled to convene on January 3, 2022, and adjourn on August 31, 2022. 2021In 2021, the legislature was scheduled to convene on December 7, 2020, and adjourn on September 10, 2021. 2020In 2020, the legislature was scheduled to convene on January 6, 2020, and adjourn on August 31, 2020.
Several state legislatures had their sessions impacted as a result of the 2020 coronavirus pandemic. The California State Legislature suspended its session, effective March 16, 2020, through May 4, 2020. The suspension had originally been scheduled to last through April 13, 2020. The legislature adjourned on August 31, 2020.[21][22] 2019In 2019, the legislature was in session from January 7, 2019, through September 13, 2019. 2018In 2018, the legislature was in session from January 3, 2018, through August 31, 2018. To read about notable events and legislation from this session, click here. 2018In 2018, the legislature was in session from January 3, 2018, through August 31, 2018. To read about notable events and legislation from this session, click here. 2017
In 2017, the legislature was in session from December 5, 2016, through September 15, 2017. 2016
In 2016, the legislature was in session from January 4 through August 31. The formal session ended on August 31, but constitutionally the session adjourned sine die on November 30. 2015
In 2015, the legislature was in session from December 1, 2014, through September 12, 2015. Major issues in 2015Major issues during the 2015 legislative session included medical marijuana, tuition in the University of California system, a proposed tax increase, internet privacy, regulation of web-based businesses, and healthcare for illegal immigrants.[23] 2014
In 2014, the legislature was in session from January 6 to August 30. Major issues in 2014Major issues during the 2014 legislative session included the biennial budget, prison overcrowding, and water bonds.[24] 2013
In 2013, the legislature was in session from December 3, 2012, to September 13, 2013. Major issues in 2013Major issues in the 2013 legislative session included property taxes for education and tax breaks for students.[25] 2012
In 2012, the legislature was in session from January 4 to August 31. 2011
In 2011, the legislature was in session from January 3 through September 9, 2011. The legislature was convened in an extraordinary session to act upon legislation that addressed the fiscal emergency proclaimed by Governor Jerry Brown (R) on January 20, 2011.[26] 2010
In 2010, the legislature was in session from January 12 to August 31. The legislature held a special session from Aug 27, 2009, to January 11, 2010. The legislature also held three other special sessions during the year on improving the tax system, the budget shortfall, and fiscal emergencies.[27] On July 28, 2010, Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger (R) issued a declaration of fiscal emergency. This is allowed under California's Constitution as approved in 2004 under proposition 58. Upon issuance of a declaration of fiscal emergency, the legislature immediately reconvened and was not able to adjourn until after the fiscal situation was resolved.[28][29] |
About legislative sessions in California
The Tenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution declares that any power not already given to the federal government is reserved to the states and the people.[30] State governments across the country use this authority to hold legislative sessions where a state's elected representatives meet for a period of time to draft and vote on legislation and set state policies on issues such as taxation, education, and government spending. The different types of legislation passed by a legislature may include resolutions, legislatively referred constitutional amendments, and bills that become law.
Article IV of the California Constitution establishes when the California State Legislature—of which the Assembly is a part—is to be in session. Section 3 of Article IV states that the legislature is to meet in regular session on the first Monday of December in each even-numbered year to organize. The legislature adjourns by November 30 of the following even-numbered year.
Section 3 also gives the governor of California the power to call special sessions of the legislature.
Legislative roles and procedures
Every state legislature throughout the country features its own internal procedures that it uses to govern itself and how it interacts with other parts of state government. Ballotpedia's coverage of internal state legislative procedures includes veto overrides, the role of the legislature in the state budget, term limits, and procedures for filling membership vacancies.
Veto overrides
- See also: Veto overrides in state legislatures
State legislatures can override governors' vetoes. Depending on the state, this can be done during the regular legislative session, in a special session following the adjournment of the regular session, or during the next legislative session. The rules for legislative overrides of gubernatorial vetoes in California are listed below.
How many legislators are required to vote for an override? Two-thirds of members in both chambers.
| Two-thirds of members in both chambers must vote to override a veto, which is 54 of the 80 members in the California State Assembly and 27 of the 40 members in the California State Senate. California is one of 36 states that requires a two-thirds vote from both of its legislative chambers to override a veto. |
Are there other special rules?
| The California Legislature has 60 days to override a veto after it has been returned by the governor.[31] |
Authority: Article IV, Section 10 of the California Constitution.
| "Each bill passed by the Legislature shall be presented to the Governor. It becomes a statute if it is signed by the Governor. The Governor may veto it by returning it with any objections to the house of origin, which shall enter the objections in the journal and proceed to reconsider it. If each house then passes the bill by rollcall vote entered in the journal, two-thirds of the membership concurring, it becomes a statute." |
Role in state budget
- See also: California state budget and finances
| California on |
The state operates on an annual budget cycle. The sequence of key events in the budget process is as follows:[32]
- Budget instructions are sent to state agencies beginning in April.
- Agencies submit their budget requests to the governor in September.
- The governor submits his or her proposed budget to the state legislature in January.
- The legislature adopts a budget in June. A majority is required to pass a budget. The fiscal year begins July 1.
California is one of 43 states in which the governor has line item veto authority.[32]
The governor is required to submit a balanced budget to the legislature. In turn, the legislature is required to adopt a balanced budget.[32]
Committees
Every state legislature and state legislative chamber in the country contains several legislative committees. These committees are responsible for studying, amending, and voting on legislation before it reaches the floor of a chamber for a full vote. The different types of committees include standing committees, select or special, and joint.
- Standing committees are generally permanent committees, the names of which sometimes change from session to session.
- Select or special committees are temporary committees formed to deal with specific issues such as recent legislation, major public policy or proposals, or investigations.
- Joint committees are committees that feature members of both chambers of a legislature.
Ballotpedia covers standing and joint committees. The California State Assembly has 33 standing committees:
- Accountability and Administrative Review Committee
- Aging and Long-Term Care Committee
- Agriculture Committee
- Appropriations Committee
- Arts, Entertainment, Sports, Tourism, and Internet Media Committee
- Banking and Finance Committee
- Budget Committee
- Business and Professions Committee
- Communications and Conveyance Committee
- Education Committee
- Elections Committee
- Emergency Management Committee
- Environmental Safety and Toxic Materials Committee
- Governmental Organization Committee
- Health Committee
- Higher Education Committee
- Housing and Community Development Committee
- Human Services Committee
- Insurance Committee
- Jobs, Economic Development, and the Economy Committee
- Judiciary Committee
- Labor and Employment Committee
- Local Government Committee
- Military and Veterans Affairs Committee
- Natural Resources Committee
- Privacy and Consumer Protection Committee
- Public Employment and Retirement Committee
- Public Safety Committee
- Revenue and Taxation Committee
- Rules Committee
- Transportation Committee
- Utilities and Energy Committee
- Water, Parks, and Wildlife Committee
Constitutional amendments
In every state but Delaware, voter approval is required to enact a constitutional amendment. In each state, the legislature has a process for referring constitutional amendments before voters. In 18 states, initiated constitutional amendments can be put on the ballot through a signature petition drive. There are also many other types of statewide measures.
The methods in which the California Constitution can be amended:
- See also: Article II and Article XVIII of the California Constitution and Laws governing ballot measures in California
The California Constitution can be amended in these ways:
- Through the process of a legislatively referred constitutional amendment. This procedure is defined in Section 1 of Article XVIII of the California Constitution. According to that section:
- Two-thirds of the membership of each chamber of the California State Legislature must propose an amendment, which then goes on a statewide ballot to be ratified or rejected by the state's voters.
- The state legislature is allowed to propose revisions (not just amendments) to the constitution.
- If measures conflict, and they both get more than 50 percent of the vote, the one with the highest number of votes prevails.
- Ratified amendments take effect the day after the election.
- Through the process of an initiated constitutional amendment, according to Section 3 of Article XVIII and Section 8 of Article II.
- Petitioners can collect signatures equaling eight percent of the most recent total number of votes cast for the office of governor to qualify a proposed amendment for the ballot.
- See Ballotpedia's page on laws governing the initiative process in California for full details on the process and requirements of an initiated constitutional amendment in California.
- Through the process of a constitutional convention. According to Section 2 of Article XVIII, if two-thirds of the members of each chamber of the state legislature agree, a question as to whether to call a convention or revise the constitution goes on the state's next general election ballot.
2025 measures:
- See also: 2025 ballot measures
Certified:
- The following measures have been certified for the ballot.
No measures to list
Potential:
- The following measures have made it through one chamber—or one session for two session states—and may appear on the ballot in 2025.
No measures to list
2024 measures:
Below is a list of measures that were referred to the 2024 ballot by the legislature or that have made it approximately halfway through the process in the legislature for referral to the ballot in 2024.
- See also: California 2024 ballot measures
Certified:
- The following measures have been certified for the ballot.
| California Remove Voter Approval Requirement for Public Low-Rent Housing Projects Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 37 (92.5%) | No votes: 0 (0.00%) | Yes: 30; No: 0 | Yes: 7; No: 0 |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 73 (91.3%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 58; No: 0 | Yes: 14; No: 0 |
| California Right to Marry and Repeal Proposition 8 Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 31 (77.5%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 30; No: 0 | Yes: 1; No: 0 |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 67 (83.8%) | No votes: 0 (0.00%) | Yes: 58; No: 0 | Yes: 9; No: 0 |
| California Vote Requirements for Initiatives Requiring Supermajority Votes Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 28 (70.0%) | No votes: 9 (22.5%) | Yes: 28; No: 1 | Yes: 0; No: 8 |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 55 (68.8%) | No votes: 19 (23.7%) | Yes: 55; No: 1 | Yes: 0; No: 18 |
| California Lower Supermajority Requirement to 55% for Local Special Taxes to Fund Housing and Public Infrastructure Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 29 (72.5%) | No votes: 10 (25.0%) | Yes: 29; No: 2 | Yes: 0; No: 8 |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 55 (68.75%) | No votes: 12 (15.00%) | Yes: 55; No: 0 | Yes: 0; No: 12 |
Potential:
- The following measures have made it through one chamber—or one session for two session states—and may appear on the ballot in 2024.
| California Flood Protection Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 75 (93.8%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 62; No: 0 | Yes: 13; No: 0 |
| California Housing Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 61 (76.25%) | No votes: 13 (16.25%) | Yes: 61; No: 0 | Yes: 0; No: 13 |
| California Parks, Environment, Energy, and Water Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 33 (82.5%) | No votes: 5 (12.5%) | Yes: 32; No: 0 | Yes: 1; No: 5 |
| House: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| California Public School and College Health and Safety Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 33 (82.5%) | No votes: 4 (10.0%) | Yes: 31; No: 0 | Yes: 2; No: 4 |
| House: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| California Farming and Food-Access Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 67 (83.8%) | No votes: 9 (11.2%) | Yes: 61; No: 0 | Yes: 6; No: 9 |
| California Drinking Water, Natural Disaster Prevention, Energy, and Workforce Development Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 63 (78.8%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 61; No: 0 | Yes: 2; No: 0 |
| California Public Education Facilities Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 66 (82.5%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 58; No: 0 | Yes: 8; No: 0 |
| California Climate and Flood Protection Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 36 (90.0%) | No votes: 2 (5.0%) | Yes: 32; No: 0 | Yes: 4; No: 2 |
| House: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| California Family Home Construction and Homeownership Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 28 (70.0%) | No votes: 9 (22.5%) | Yes: 28; No: 2 | Yes: 0; No: 7 |
| House: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| California Fentanyl Overdose Prevention Bond Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 76 (95.0%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 59; No: 0 | Yes: 17; No: 0 |
| California Labor Standards for Employees of the University of California Regents Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 67 (83.75%) | No votes: 7 (8.75%) | Yes: 61; No: 0 | Yes: 6; No: 7 |
| California Amend Proposition 209 to Authorize State Programs Based on Race, Ethnicity, National Origin, or Genders Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 62 (77.50%) | No votes: 18 (22.50%) | Yes: 62; No: 0 | Yes: 0; No: 18 |
| California Authorize Multiple Property Tax Exemptions for Veterans Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: 27 | Yes votes: 39 (97.5%) | No votes: 0 (0.0%) | Yes: 31; No: 0 | Yes: 8; No: 0 |
| House: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| California Remove Involuntary Servitude as Punishment for Crime Amendment | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: 54 | Yes votes: 68 (85.0%) | No votes: 4 (5.0%) | Yes: 62; No: 0 | Yes: 6; No: 4 |
| California Allow Candidates to Use Public Money from Dedicated Funds Measure | Democrats | Republicans | |||
| Senate: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
| House: | Required: | Yes votes: (%) | No votes: (%) | Yes: ; No: | Yes: ; No: |
See also
| Elections | California State Government | State Legislatures | State Politics |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
External links
Footnotes
- ↑ According to the Chief Clerk of the California State Assembly, "Assembly Members who were first elected to the State Legislature on or after the passage of Proposition 28 may serve 12 years in the Assembly, or a combination of service in the Assembly and Senate as long as the combined terms do not exceed 12 years. However, Members elected to the State Assembly prior to the passage of Proposition 28 may serve a maximum of three two-year terms established by the passage of Proposition 140, in 1990."
- ↑ California State Assembly Office of the Chief Clerk, "Elected Officials," accessed January 22, 2019
- ↑ California State Assembly, "Glossary of Legislative Terms," accessed February 9, 2021
- ↑ California Legislature, "Qualifications for State Legislature," accessed February 10, 2023
- ↑ Note: This text is quoted verbatim from the original source. Any inconsistencies are attributable to the original source.
- ↑ California Secretary of State, "Key Dates and Deadlines," accessed June 19, 2017
- ↑ California Secretary of State, "Key Dates and Deadlines," accessed April 18, 2017
- ↑ Follow the Money, "California Assembly 2010 Campaign Contributions," accessed April 21, 2015
- ↑ Follow the Money, "California 2008 Candidates," accessed June 18, 2013
- ↑ Follow the Money, "California 2006 Candidates," accessed June 18, 2013
- ↑ Follow the Money, "California 2004 Candidates," accessed June 18, 2013
- ↑ Follow the Money, "California 2002 Candidates," accessed June 18, 2013
- ↑ Follow the Money, "California 2000 Candidates," accessed June 18, 2013
- ↑ California Legislative Information, "Article IV Legislative (Sec. 1 - Sec. 28)," accessed February 9, 2021
- ↑ California Legislative Information, "California Code," accessed February 9, 2021 (Statute, 1773-California Government Code)
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 All About Redistricting, "California," accessed April 21, 2015
- ↑ Politico, "California’s new congressional map boosts Democrats," Dec. 21, 2021
- ↑ Lake County News, "California Citizens Redistricting Commission delivers maps to California Secretary of State," Dec. 28, 2021
- ↑ California Secretary of State, "California Redistricting"
- ↑ "Current Status of Commission’s Final Certified District Maps". California Citizens Redistricting Commission. 2011. http://wedrawthelines.ca.gov/maps-final-drafts.html. Retrieved on 20 February 2012.
- ↑ The Los Angeles Times, "California lawmakers approve $1 billion in funding and legislative hiatus due to coronavirus," March 16, 2020
- ↑ Politico, "California Legislature plans May 4 return as coronavirus disrupts public life," April 3, 2020
- ↑ The Sacramento Bee, "Key issues for returning California Legislature," January 5, 2015
- ↑ acwa.com, "2014 Legislative Year Begins in Sacramento," January 6, 2014
- ↑ San Francisco Chronicle, "Calif. Democrats ponder their new power," December 2, 2012
- ↑ ncsl.org, "2011 Legislative Sessions Calendar," accessed April 21, 2015
- ↑ ncsl.org, "Session dates for California legislature, 2010," accessed April 21, 2015
- ↑ Office of the Governor, "Gov. Schwarzenegger Declares State of Emergency, Issues Executive Order to Impose Furloughs Due to Cash Crisis Caused By Budget Impasse," accessed August 24, 2010
- ↑ Office of the Governor, "Executive Order S-12-10," accessed August 24, 2010
- ↑ Find Law, "Tenth Amendment - U.S. Constitution," accessed May 20, 2017
- ↑ calafco.org, "Legislative Procedure," accessed July 3, 2017
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 National Association of State Budget Officers, "Budget Processes in the States, Spring 2021," accessed January 24, 2023
| |||||||||||
 |
State of California Sacramento (capital) |
|---|---|
| Elections |
What's on my ballot? | Elections in 2024 | How to vote | How to run for office | Ballot measures |
| Government |
Who represents me? | U.S. President | U.S. Congress | Federal courts | State executives | State legislature | State and local courts | Counties | Cities | School districts | Public policy |